Free PBX (Asterisk)
The Asterisk software includes many features available in proprietary PBX systems: voice mail, conference calling, interactive voice response (phone menus), and automatic call distribution. Users can create new functionality by writing dial plan scripts in several of Asterisk’s own extensions languages, by adding custom loadable modules written in C, or by implementing Asterisk Gateway Interface (AGI) programs using any programming language capable of communicating via the standard streams system (stdin and stdout) or by network TCP sockets.
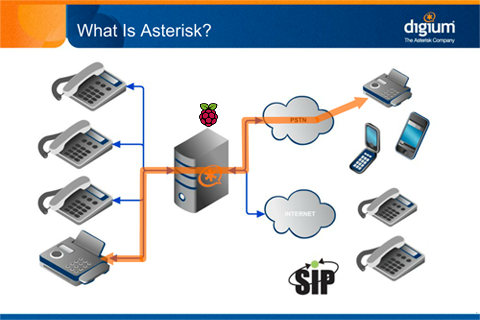
Asterisk supports a wide range of Voice over IP protocols, including the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), the Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP), and H.323. Asterisk can interoperate with most SIP telephones, acting both as registrar and as a gateway between IP phones and the PSTN. The Inter-Asterisk eXchange (IAX2) protocol, RFC 5456, native to Asterisk, provides efficient trunking of calls among Asterisk PBXes, in addition to distributed configuration logic, and call completion to VoIP service providers who support it. Some telephones support the IAX2 protocol directly (see Comparison of VoIP software for examples).
By supporting a mix of traditional and VoIP telephony services, Asterisk allows deployers to build new telephone systems, or gradually migrate existing systems to new technologies. Some sites are using Asterisk servers to replace proprietary PBXes; others to provide additional features (such as voice mail or voice response menus, or virtual call shops) or to reduce costs by carrying long-distance calls over the Internet (toll bypass).
Asterisk was one of the first open source PBX software packages.
